Southern California, famous for its sun-kissed beaches and mild winters, has found itself under siege from a rare and intense winter storm. This unusual weather phenomenon has not only disrupted daily life but has also led to the declaration of a state of emergency in California. Here, we delve deep into the storm’s impact on Southern California, focusing on its effects, underlying causes, and what it might signal for the future.
California Winter Storm Triggers State of Emergency
On January 25, 2024, California Governor Gavin Newsom declared a state of emergency as the winter storm gained momentum. The extreme weather conditions forced state and local authorities to spring into action to protect public safety and reduce potential damage.
Emergency Services and Response
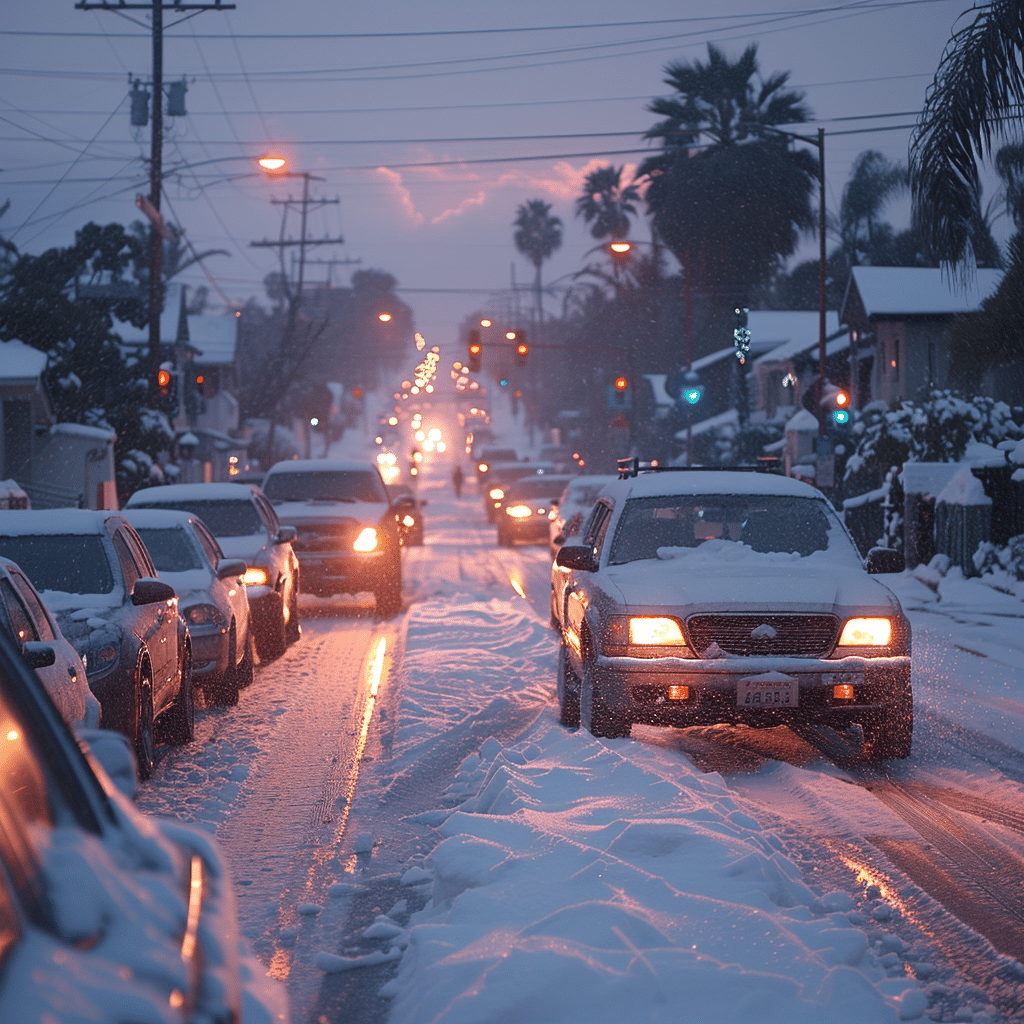

Southern California Winter Storm: The Causes Behind the Chaos
The conditions that precipitated this storm are both complex and multi-faceted. Climate scientists have identified several critical factors contributing to this extraordinary event.
Atmospheric River
A significant factor was a narrow corridor of concentrated moisture known as an atmospheric river. This corridor funneled vast quantities of water vapor from the Pacific Ocean into Southern California, leading to intense rains and snowfall.
El Niño Effect
The persistent El Niño phenomenon added to the storm’s severity. Warmer ocean temperatures contributed to atmospheric instability, which in turn enhanced storm development and precipitation.
Jet Stream Disruption
The polar jet stream dipped further south than usual, creating a pathway for cold air to mix with the warm, moisture-laden air from the atmospheric river. This clash resulted in extreme weather conditions.
| Date | Event Description | Location | Impact and Notes |
| Mar 2, 2024 | Worker digs out snow from a home north of Lake Tahoe during a powerful, multiple-day winter storm in the Sierra Nevada. | Truckee, California | Significant snow accumulation, impacting homes and infrastructure. |
| Mar 4, 2024 | A blizzard dumps several feet of snow across California’s Sierra Nevada, leaving snow piled above cars and snow drifts reaching rooftops. | South Lake Tahoe, Calif. | Multiple feet of snow, major road closures, and significant disruptions. |
| Winter Season | Areas across California, especially in Northern regions, support snow activities such as skiing, snowboarding, and tobogganing. | Northern and Southern CA | Popular destinations for winter sports and recreational activities. |
| Mar 14, 2024 | La Niña impacts felt with drier, warmer-than-average conditions expected across Southern California during winter. | Southern California | Reduced precipitation, warmer temperatures, affecting water supply and agriculture. |
| Sep 9-10, 2022 | Tropical Storm Kay transitioned into a post-tropical cyclone, bringing heavy rainfall, mudslides, and debris flow. | Southern California | Mount Laguna saw 5.85 inches of rain; one fatality in Forest Falls due to mudslide. |
| Key Term | Definition | Impact | |
| La Niña | Climatic phenomenon | Typically causes drier, warmer winters in Southern California, affecting local ecosystems and agriculture. | |
| Blizzard | Severe snowstorm with high winds | Leads to significant snow accumulation, transportation disruptions, and potential infrastructure damage. | |
| Post-Tropical Cyclone | Remnant of a tropical storm | Can bring heavy rainfall and resultant mudslides, as seen with Tropical Storm Kay. | |
| Activity | Region | Notes | |
| Skiing | Northern and Southern CA | Popular in winter, especially in areas like Lake Tahoe. | |
| Snowboarding | Northern and Southern CA | Requires heavy snowfall, which can be impacted by weather phenomenon like La Niña. | |
| Tobogganing | Northern and Southern CA | Fun family activity, possible when snow conditions are ideal. | |
| Digging out Snow | Sierra Nevada region | Essential during heavy snowfall to ensure access to homes and roads. |
Impact on Infrastructure: Roads, Schools, and Power Outages
The Southern California winter storm wreaked havoc on the region’s infrastructure, causing significant disruptions and damage.
Road Closures
Major highways, including Interstate 5 and Highway 101, were closed due to heavy snow and landslides. Caltrans reported over 200 incidents of road debris and structural damage.
School Closures
School districts in counties like Los Angeles, San Bernardino, and Riverside shut down classes for several days. The Los Angeles Unified School District (LAUSD) reported significant damages to several school buildings, mainly from flooding and falling trees.
Power Outages
Southern California Edison confirmed that over 500,000 customers experienced power outages. High winds and falling branches severed power lines, complicating efforts to restore electricity amid ongoing severe weather.
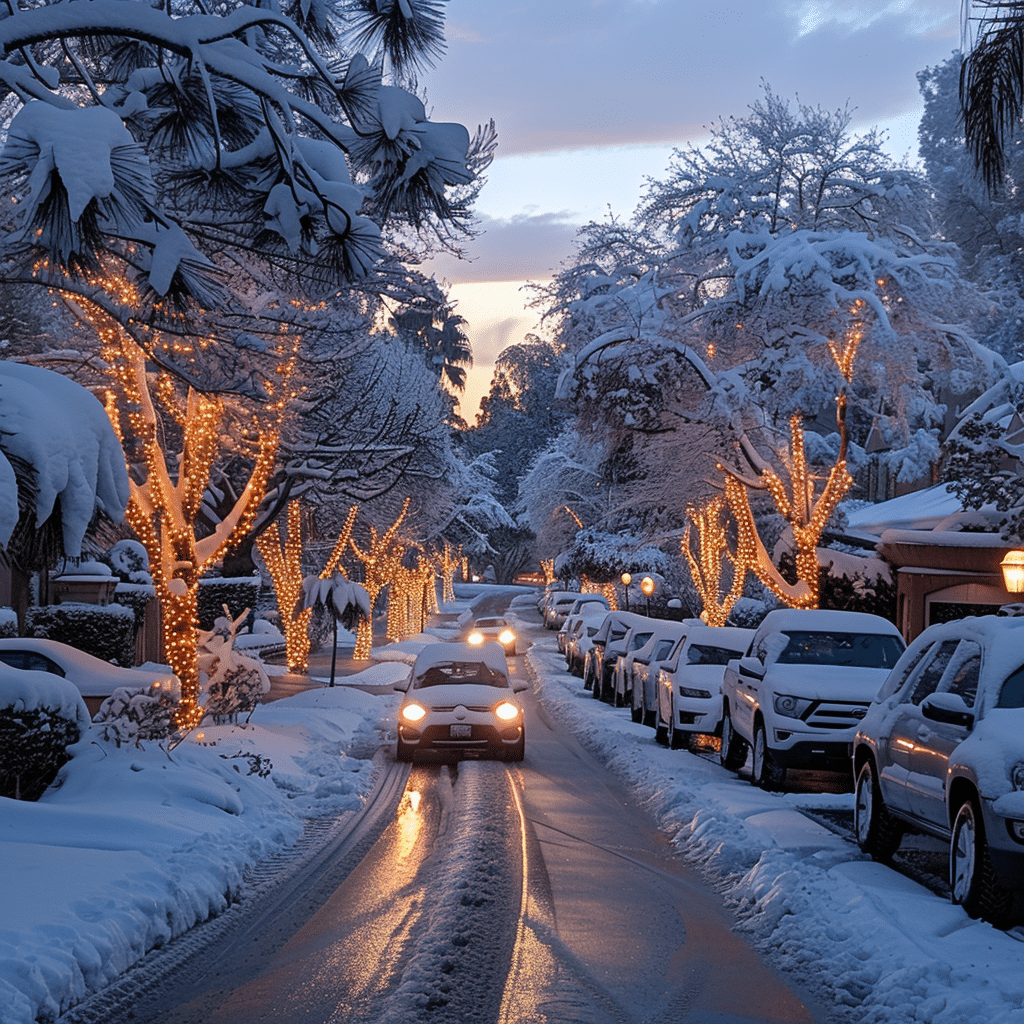
Economic Consequences: Businesses and Agriculture
The storm’s economic impact has been substantial, affecting urban businesses and rural agricultural sectors.
Retail and Small Businesses
Numerous small businesses in downtown Los Angeles and nearby areas faced significant losses due to closures and decreased customer traffic. The Southern California Chamber of Commerce estimated millions in lost revenue.
Agricultural Losses
The Central Valley, a critical agricultural hub, suffered severe crop damage. Citrus and avocado farms reported losses from prolonged freezing temperatures and waterlogged fields. Farmers are now bracing for long-term impacts on crop yields and quality.
Community Resilience and Future Preparedness
In the face of widespread disruption, Southern California communities have demonstrated remarkable resilience. Neighborhoods came together to support those in need, and local organizations played a pivotal role in relief efforts.
Community Efforts
Volunteer groups such as the Red Cross and the Southern California Resilience Coalition coordinated efforts to distribute food, blankets, and medical supplies in affected areas.
Long-Term Planning
This storm has underscored the need for better infrastructure planning and preparedness. Urban planners and policymakers advocate for improved drainage systems, robust emergency response protocols, and enhanced public education about severe weather preparedness.
Analyzing the Long-Term Implications
The Southern California winter storm of 2024 underscores the increased unpredictability of weather patterns, driven by climate change. Scientists warn that such extreme weather events may become more frequent, warranting a reevaluation of regional preparedness and environmental strategies.
Climate Change Adaptation
The storm highlights the critical need to invest in climate resilience. This includes upgrading infrastructure to withstand extreme weather, developing comprehensive emergency response plans, and taking proactive measures to reduce carbon emissions.
Public Awareness
Educating the public on the potential for extreme weather and the steps they can take to stay safe is crucial. Enhanced communication strategies and early warning systems will be vital in minimizing the impact of similar events in the future.
In conclusion, the Southern California winter storm has been a stark reminder of nature’s unpredictability. Yet, amid the challenges, the region’s response has showcased human resilience and ingenuity. As Southern California works to recover and rebuild, there’s an opportunity to learn, strengthen community bonds, and better prepare for future challenges.
Southern California Winter Storm Brings Chaos
Amazing Trivia About the Southern California Winter Storm
Believe it or not, the Southern California winter storm has conjured some bizarre and fascinating stories. For example, amidst the chaos, fans were engrossed in the unexpected event of Bayern Munich Vs Leverkusen Lineups, which seemed almost out of place given the weather mayhem. As nature showed its muscle, there were tales of people rushing into fast food spots, indulging in comfort foods like Burger King Milkshakes to calm their blizzard-battered nerves.
In another curious twist, Pete Salazar jr, known for his inspiring community work, reportedly helped rescue several stranded motorists during the storm. His selfless actions were nothing short of heroic, as he braved the severe conditions to lend a hand. On a lighter note, did you ever stop to think about the calorie count in your winter comfort foods? Many storm shelter-goers were shocked to learn the number of calories in a regular Mcflurry. The storm brought chaos, but also moments that brought people together.
Naturally, the storm affected travel plans for many Southern Californians. Surprisingly, some folks with pending travels to sunny destinations, like those checking out this Curacao island map, had to put their plans on hold. With airports in disarray, even avid travelers couldn’t escape the unexpected freeze. Speaking of which, many people wondered just Where Curacao Is located as they dreamt of escaping the winter wrath to a more tropical location.
Additionally, as storms bring a sudden pause to routines, some took the time to catch up on entertainment news. Stories like Dalvin Cook ‘s move To The Jets gave them something to cheer about, amidst the chilly gloom. It’s funny how a storm can shift your focus, making you appreciate the small things like sports updates and movie marathons. Lastly, the storm even led to quirky community discussions; people equated the sudden social gatherings in shelters to a human gathering cult, highlighting the strange ways in which folks find solace and camaraderie during such unprecedented times.

Where in California did they get 10 feet of snow?
Areas near Lake Tahoe, especially Truckee, saw up to 10 feet of snow dumped during a powerful winter storm in early March 2024.
Where was the big snow storm in California?
The big snowstorm in California hit the Sierra Nevada region, covering areas such as South Lake Tahoe and Truckee with several feet of snow at the beginning of March 2024.
Will Southern California get snow?
Southern California generally doesn’t get much snow due to its typically dry and warm winter conditions, influenced by phenomena like La Niña.
What does a La Nina winter mean for Southern California?
A La Niña winter for Southern California typically means drier and warmer-than-average weather, so don’t expect much snow in this region.
What state has 16 feet snow?
California, specifically the Sierra Nevada mountains, is known for getting some of the heaviest snowfall in the US, sometimes reaching up to 16 feet.
What California town is buried in snow?
Truckee, near Lake Tahoe in California, has recently been buried under several feet of snow resulting from a major winter storm in March 2024.
What part of California got 12 ft of snow?
The Sierra Nevada region near Lake Tahoe in Northern California received up to 12 feet of snow with the recent massive storm.
What year did California get the most snow?
The winter of 2023-2024 saw some of the most significant snowfall in California’s history, particularly in the Sierra Nevada region.
Where was the worst snow storm in history?
One of the worst snowstorms historically known affected the Sierra Nevada mountains, often seeing feet of snow accumulation from severe winter weather.
Does it snow in Hawaii?
Yes, it actually snows in Hawaii, but only on the summits of its tallest mountains like Mauna Kea and Mauna Loa.
Did California get 7 ft of snow?
Yes, parts of California received around 7 feet of snow in the Sierra Nevada region during the big storm in early March 2024.
Does Florida get snow?
Snow in Florida is extremely rare, but it has happened on very few occasions, typically as light flurries with no significant accumulation.
Will 2024 be a hot summer in California?
It’s tough to predict exact summer temperatures, but with climate trends showing warming patterns, it wouldn’t be surprising if California has a hot summer in 2024.
Why is the Pacific Ocean so cold?
The Pacific Ocean feels cold mainly because of the California Current, which brings cool water down from the Arctic regions along the West Coast.
Is California getting wetter?
California seems to be getting wetter recently, particularly during certain seasons, possibly due to changing climate patterns.
Where did it snow 12 feet in California?
Near Lake Tahoe in the Sierra Nevada region of Northern California, over a stretch of days in early March 2024, saw up to 12 feet of snow.
Where in California did they get 7 feet of snow?
Regions near Lake Tahoe, especially Truckee in Northern California, got buried under about 7 feet of snow during the recent storm in March 2024.
Where is the deepest snow in California?
The deepest snow in California often piles up in the Sierra Nevada mountains, especially during heavy winter storms.
Where in California did they get 50 feet of snow?
It’s unlikely any spot in California has hit 50 feet of snow, but mountains in the Sierra Nevada can accumulate many feet over the winter season.



